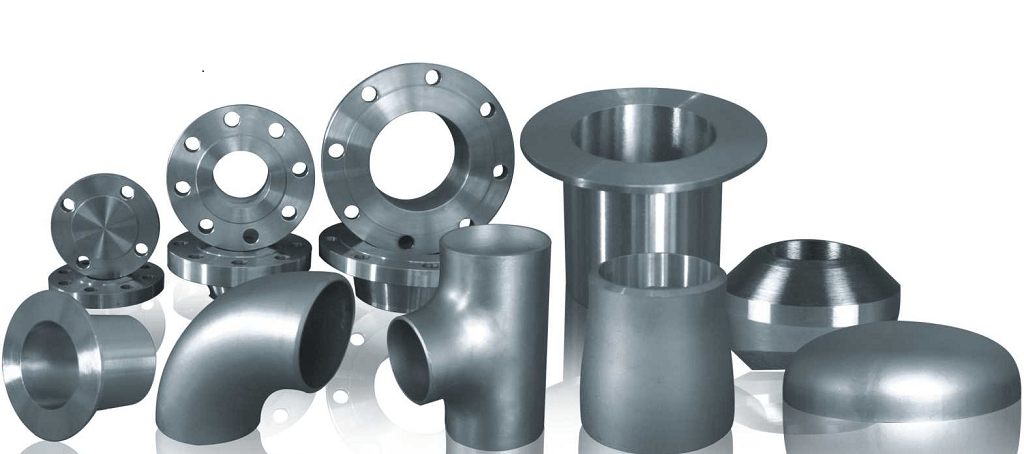
Introduction to Pipe Fittings
Pipe Fittings are an important piping component that helps in changing the direction of the flow such as elbows, tees, changes the size of the pipe such as reducers, reducing tees, distribute the water supply from the main pipe to other pipes of equal size or lower size, etc. connect different components such as couplings and stop the flows such as caps. In plumbing, many types of fixtures are joined with the help of various types of material such as metallic or plastic, as per the requirement. Pipe fittings vary depending on the type of pipe used. Pipe fittings basically include the range of components that are used to connect pipe ends for in-line, multi-port, offset and mounting configurations. Pipe fitting cross sections are mostly, but not always, circular in shape to match with the pipe section with which they are connected.
As one of the biggest manufacturer of steel pipes and pipe fittings manufacturer in India, Metallica carries inventory of over 15,000 tons in its warehouses in Mumbai, Maharashtra India.
Types of Pipe Fittings
Fittings are divided into the following 4 groups:
- Buttweld (BW) fittings whose dimensions, dimensional tolerances et cetera are defined in the ASME B16.9 standards. Light-weight corrosion resistant fittings are made to MSS SP43.
- Socket Weld (SW) fittings Class 3000, 6000, 9000 are defined in the ASME B16.11 standards.
- Threaded (THD), screwed fittings Class 2000, 3000, 6000 are defined in the ASME B16.11 standards.
- Flanges manufactured in compliance with ASME, DIN, and EN standards
- Double Ferrule Compression Fittings
- Instrumentation Tube Fittings
Buttweld Pipe Fittings
- A butt weld pipe fitting is a type of pipe fitting, which is designed to be welded on site to connect pipes together. Welding of a buttweld pipe fitting to pipes or other fittings is generally done to allow change in direction of the piping system. Buttweld fittings are generally identified or inquired in nominal pipe sizes with specified pipe schedule. Buttweld fitting’s dimensions and tolerances are defined as per ASME B16.9 standard. All buttweld pipe fittings have beveled ends as per ASME B16.25 standard. This helps create full penetration weld without any extra preparation needed for the butt weld fitting.
- Manufacturing buttweld fittings – A butt weld pipe fitting is made by the process of hot forming that includes bending and forming to shape. The starting material of butt weld fitting is a pipe that is cut to length, heated and molded into specific shapes by means of dies. Heat treatment is also done to remove residual stresses and obtain desired mechanical properties. Sch 10 fittings are also more common in stainless steel butt weld fitting, while SCH 40 is common for carbon steel butweld fittings.
| Pipes Bends | |
| Size | 3″-48″ |
| Radius | 3D, 4D, 5D, 6D, 8D, 10D |
| Angles | 22.5Deg, 30Deg, 45Deg, 60Deg, 90Deg |
| Pipe Fitting Standard | ANSI B16.9, ANSI B16.11, ANSI B16.28, DIN 2605, DIN2615, DIN2616, JIS B2312, JIS B2313 |
| Pipe Fitting Material | |
| Carbon Steel | ASTM A 234 WPB, A420 WPL1, WPL3, WPL6, ASTM A860 WPHY 42, WPHY52, WPHY60, WPHY65, WPHY70 |
| Stainless Steel | ASTM A403 WP304/304L, WP316/316L, WP321, WP347 |
| Alloy Steel | ASTM A234 WP1, WP5, WP9, WP11, WP12, WP22, WP91 |
| Duplex & Super Duplex Steel | ASTM A815 UNS S31803, UNS S32750, UNS S32760 |
| Pipe Fitting Schedule | |
| Carbon Steel & Alloy Steel | STD, XS, XXS, SCH10-SCH160 |
| Stainless Steel | SCH5S, 10S, 40S, 80S |
| Pipe Fitting Size | |
| Carbon Steel | 1/2″-96″ |
| Stainless Steel | 1/2″ – 24″ (Seamless and Welded), 26″ – 72″ (Welded) |
- All our products are supplied with Test certificates as per EN 10204 3.1
Forged Pipe Fittings
- Threaded Pipe Fittings – 90° Elbow, 45° Elbow, Threaded Tee, Threaded Cross, Full Coupling, Half Coupling, Reducing Coupling, Pipe Cap, Hex Head Bushing, Hex Head Plug, Square Head Plug, Round Head Plug, Threaded Union, Hex Nipple, Bull Plug, Boss, Swage Nipple, Pipe Nipple, Adapter, Union (Male x Female), Branch Outlet, 90° Elbow Outlet, Threaded Street Elbow, Threaded Lateral Tee, Lateral Outlet, Nipple Branch Outlet
- Socket Weld Pipe Fittings – 90° Elbow, 45° Elbow, Tee, Cross, Full Coupling, Half Coupling, Pipe Cap, Union, Reducer Insert, Boss, Branch Outlet, 90° Elbow Outlet, 45° Lateral Tee, Lateral Outlet, Branch Outlet Butt Weld, 90° Elbow, Outlet Butt Weld, Lateral Outlet Butt Weld, Nipple Branch Outlet Butt Weld
- Click on the above names, to view dimensions of respective products
Metallica is a well known manufacturer and supplier of forged pipe fitting for the clients from oil and gas, petrochemicals, railway, construction and other industries. We manufacture different size and shapes of forged pipe fittings by open die forging, closed die forging and drop forging. Our main products include socket weld and threaded pipe fittings in size range of 1/4″ to 4″ (6mm-100mm), with pressure rating of 2000LBS, 3000LBS, 6000LBS, and 9000LBS. The most common and materials include ASTM A105, ASTM A182 F304, F316, F304L, F316L, and A182 F5/F9/F11/F22/F91. In nickel alloys we produce socket welded and threaded pipe fittings in various grades such as Alloy 200, 201, 400, K500, 600, 625, 800H/HT, 825, X-750, C276, Hastelloy B & C22.
Forged socket weld and threaded pipe fittings are generally used for small size pipes and piping systems (generally below 4 inches in diameter for Class 3000, and below 2 inches for fittings in class 6000 and 9000). Forged pipe fittings are manufactured by forging, followed by heat treatment and machining solid steel as per ASME B16.11 and other dimensional standards. For bigger size piping systems buttweld pipe fittings produced as per ASME B16.9 are used.
Product Specification for Forged Pipe Fittings
| Product | Forged Pipe Fittings |
| Connection | Screwed or Threaded (M/F), Socket Weld |
| Type | Pipe Union, Cross, Elbow, Tee, Half Coupling, Full Coupling, Branch Outlets, Forged Plug, Hexagon Bushing, Plugs, Inserts, Caps |
| Size | 1/2″ to 4″ |
| Pressure Rating | 2000#, 3000#, 6000#, 9000# or 2000LB, 3000LB, 6000LB, 9000LB |
| Process method | Forged, CNC Machined |
| Standards: | ASME/ANSI B16.11, MSS SP 83, MSS SP 97, MSS SP 95 |
| Certification | EN 10204 3.1 |
- Forged pipe fittings are available in both socket weld and threaded ends.
Forged Fittings Materials & Grades
| Carbon Steel | ASTM A105/N, ASTM A350LF2, LF3, LF6 |
| Duplex | 2205(F51/60), 2507(F53) |
| Chrome Moly | SA182, F1, F5, F5a, F9, F9l, F11, F12, F22 |
| Stainless Steel | 304/L/H, 316/L/H, 310, 317L, 321/H, 347/H, 410, 416, 420, 17-4, 440, Alloy 20 |
| Nickel Alloys | 200, 201, 400, K500, 600, 625, 800H/HT, 825, X-750, C276, Hastelloy B & C22 |
- Forged pipe fittings are also available in other grades on request
Flanges
- A steel flange (forged, cut from plate, or rolled) comes in a variety of shapes and sizes to suit different applications. A flange is usually in the shape of a round disc and is used to connect two pipes together or to connect a pipe to a pressure vessel, valve, pump, integral flanged assembly or other component. A flange comes with holes for bolts around the rim. Bolts are used to connect two flanges which are typically attached to pipe ends with a gasket in between.
- Flanges are available in multiple shapes, as welding neck (the pipe is welded to the collar of the flange), threaded (the pipe is screwed on the flange), socket weld (fillet welds connections), lap joint (for connections using stub ends), slip on, etc. A flange can also be a plate for covering or closing the end of a pipe. This is called a blind flange. Thus, flanges are considered to be internal components which are used to support mechanical parts.
- The ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47 specifications cover US standard pipe flanges, the EN 1092-1 specification covers European steel flanges.
- A flange can be produced and designed to the specific pressure ratings; 150lb, 300lb, 400lb, 600lb, 900lb, 1500lb and 2500lb.
What are the Various Types of Flanges?
A flange can be characterized and classified in various ways such as:
-Types of Connection
-Flange facing Types
-Pressure Temperature Ratings
-Material Types
- Click on the above names, to view details of respective products
Some of the Most Widely Used Pipe Fittings for Piping Systems
There are different types of pipe fitting used in piping.
1. Adapters: Adapters are an extremely important pipe fitting that extend or terminate pipe runs. They are used to connect dissimilar pipes. These fittings are somewhat similar to pipe couplings, with the difference that they connect pipe of different types, one of which is an IPS (Iron Pipe Size). 
2. Elbows: Elbows, also known as “ells,” are used to change the direction of the flow. 
3. Couplings: A coupling is a pipe fitting used to stop leakages 
4. Olet: These fittings are used when the standard size of the fittings fails to serve the purpose. Whenever branch connections are required in size where reducing tees are not available and/or when the branch connections are of smaller size as compared to header size, olets are generally used.
5. Union: This type of pipe fitting is almost similar 
6. Nipple: 
could be used for short extension of plumbing lines. It can also be used for connecting two fittings within small distance.
7. Reducer: This pipe setting is used to reduce the flow size of the pipe from the bigger to smaller one. There are two kinds of reducers- concentric reducer and eccentric reducer. It is used to connect pipes of different diameters. A
reducer may be of various types like reducer tee, reducer elbow and reducer socket. 
8. Tee: This T-shaped pipe fitting used in the plumbing
9. Cross: Cross is also known as four-way pipe fitting. A cross has one inlet and three outlets (or vice versa). Generally, crosses are not used in process piping to transport fluid. But forged crosses are common in the fire water sprinkler line.
10. Flanges: A flange is another pipe fitting used to connect pipes,
11. Caps & Plugs: A cap, as its name suggests, is a cap that goes over the end of a pipe, creating a dead end. Plugs also stop up a pipe or tube system, but are plugged, like a stopper, into the end of the pipe.
12. Bushings: 
13. Wyes: It is a type of Tee which has the branch at a 45° angle, or an angle other than 90°. Wye tee allows one pipe to be joined to another at a 45° angle. This type of tee reduces friction and turbulence that could hamper the flow. Wye tee is also known as a lateral.
14. Valves: Valves are used in the plumbing system to stop 
15. Barb:
A “barb” or “hose barb” fitting is used to connect flexible hose or tubing to pipes. A barb fitting typically has a male-threaded end used to mate with female threads. The other end of the fitting has either a single- or multiple-barbed tube having a tapered stub with ridges, which is inserted into a flexible hose to secure it.
16. Diverter tee: 
Various types of pipe joints are as follows:-
- Threaded joint
- Welded joint (butt welded, socket welded)
- Brazed joint
- Soldered joint
- Grooved joint
- Flanged joint
- Compression joint