Stainless Steel Pipe Manufacturers, Suppliers, Stockist – Seamless Pipes, Welded Pipes, Coiled Tubes, Square Pipes, Rectangular Pipes, Electropolished Pipes
- Metallica is one of the biggest stainless steel pipe suppliers and manufacturers in India, with over 250 customers in India and overseas. We are bulk buyers and exporters of stainless steel pipes from our factories in India and overseas (USA, Japan, Korea, Europe), and are able to give you the best price and quality just in time.
- Buy Quality Stainless Steel Pipes from an Inventory of 1000 tons in India! Metallica is the largest importer of stainless steel seamless pipes and one of the biggest supplier of stainless steel pipes India. We are the first company in India, to offer our customers a price guarantee. Metallica manufactures and supplies stainless steel pipes and tubes for critical applications in industries like oil & gas, aviation, aerospace, petrochemical, natural gas, paper making, industrial gas, heat exchange and others.
- Stainless steel pipes are manufactured as per ASTM A312, 358, 778, 928, ASTM B619, and B725. All materials are also available in accordance to equivalent DIN/ EN standards and grades. We are manufacturers, stockholder and suppliers of seamless & welded stainless steel pipes in various standards such as ASTM A213, ASTM A312, ASTM A269, ASTM A778, ASTM A789 and grades including 304/304L, 310S, 316/316L, 321/321H, 347/347H, 904L, Alloy 20, Duplex & Super Duplex.
- All our stainless steel pipes and tube products are supplied with 3.1 specific test certificates, according to EN 10204. Certification according to 3.2 can be agreed at the time of ordering.


Complete Production & Stock Range of Stainless Steel Pipes
| Product | Stainless Steel Pipes |
| Pipe Standards | ASTM A213, ASTM A312, ASTM A269, ASTM A778, ASTM A789, A554 |
| Grades | 304/L, 316/L, 201, 202, 301, 347/H, 316Ti, 309S, 310S, Duplex, Super Duplex, 904L, 317L |
| OD | 6mm – 610mm |
| Thickness | 1.0mm to 40mm |
| Length | 5.8m, 6, Custom Lengths |
| Technology | Hot Rolled, Cold Drawn, Extruded, Cold Finished, Heat Treated |
| Finish | Annealed & pickled, Bright Annealing, Polished |
| Test Certificate | EN 10204 3.1 |
| Pipe Ends | Plain End, Bevel Ends |
Various Types & Grades of Stainless Steel Pipes & Tubes Available on Sale
Chemical and Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steel Pipes
What is a Stainless Steel Pipe? Difference in Carbon & Stainless Steel Pipe!
Stainless steel is a versatile material comprised of a steel alloy and a small percentage of chromium—the addition of chromium adds to the material’s corrosion resistance, a trait that earned stainless steel its name. Because stainless steel is also low-maintenance, oxidation resistant, and doesn’t affect other metals it comes in contact with, it is frequently used in a large array of applications, especially in piping and tubing manufacturing. Metallica is engaged in manufacturing stainless steel pipes using best quality components and implementing latest technologies. These are manufactured as per international industrial standards and are widely acclaimed for durability and reliability following the requirements of our clients.
Features:
- Desirable Hardness
- High Electrical Conductivity
- Low Temperature
Carbon steel and stainless steel have the same basic ingredients of iron and carbon. Their main difference is alloy content—carbon steel has under 10.5 percent alloy content, while stainless steel must contain 10.5 percent chromium or more. That essential difference is what gives carbon steel and stainless steel their distinct physical characteristics is as below:
| Carbon Steel | Stainless Steel |
| Vulnerable to rust | Resistant to rust |
| Brittle | Less Brittle |
| Wear-resistant | Less wear-resistant |
What is the Difference Between a Pipe & a Tube?
Although pipes and tubes may look similar, they are in fact quite different in nomenclature and sizing. Remember that pipes and tubes are rarely interchangeable. The difference between pipe and tube include:
- Shape – Pipes are always round, whereas tubes can be square, rectangular or round.
- Tolerances – Pipe tolerances are set but not too restrictive. Tube tolerances are very strict – (Production process is generally lengthy and involves many quality checks around key dimensional parameters such as straightness, roundness, wall thickness, surface, etc.).
- Measurement – Pipes are generally measured by the inside diameter (ID), often called the “nominal” diameter, and a “schedule”, which refers to the wall thickness whereas for tubes, the outer diameter (OD) and wall thickness, which are exact measures in inches or millimeters roughly corresponds to the tube size. For tubes, the difference between the outside diameter and the wall thickness, multiplied by two, defines the inside diameter of the tube.
- Rigidity – Although copper and brass tubes can be shaped relatively easily, tubes are are typically rigid. Pipes, on the other hand, are invariably rigid and cannot be shaped without special equipment.
- Applications – Pipes are used in all process fluids and services. Tubes are generally used in tracing lines, tubes for heat exchanger, fired heater and in instrument connection. Tubes are also used as primary load bearing member in steel structure for the civil application.
- Metal Types – Tube is available in hot rolled steel and cold rolled steel. Pipe is typically black steel (hot rolled). Both items can be galvanized.
- Size – Pipes are typically larger than tubes.
- Strength – Tubes are stronger than pipes.
Categories of Stainless Steel Pipes
Based on the end use of the pipe, stainless steel piping is broken down into several categories.
- Seamless Pipe: A seamless pipe is a pipe that does not contain any seams or weld joints. It’s capable of standing up to intense levels of pressure and also temperatures thanks to the metal itself. It’s used in a wide variety of different oil and gas applications, but they are also used in mechanical and engineering industries too. This makes seamless pipes rather versatile and they are always inspected with high levels of precision to ensure the quality of the material.
- Welded Pipe: Welded pipes can be used in virtually every industry thanks to its flexibility. However, they fare better in corrosion resistance as opposed to withstanding pressure. Because of the materials used and the lightweight nature of welded pipes, they’re far more cost-effective than most other piping methods and offer the best value for your money.
- Flanges: Pipe flanges are another important part of your overall piping setup. These come in many forms such as slip-ons, blinds, lap joints, threaded and semis. These are made from durable and sturdy materials to ensure their reliability and high-quality products are always used when creating pipe flanges.
- Spectacle Blinds: For permanent or long-term solutions that allow for isolation of piping sections, spectacle blinds, spades and spacers are used for convenience. If a piece of machinery or piping section needs to be inspected, then spectacle blinds are used so that you can isolate a certain part of the piping in order to maintain a larger system. Since this is an incredibly important role that is crucial to your safety, it’s recommended to rigorously test the reliability of your spectacle blinds if you want to remain safe.
- Stainless Steel Piping: For tubing and piping applications, type 304 stainless steel is a common selection because it is highly chemical- and corrosion-resistant. However, type 304 stainless steel is not compatible with applications where temperatures fall between 800 and 1640 degrees Fahrenheit (F) because it is prone to carbide precipitation, a result of the material’s .08 percent carbon content limit. Stainless steel type 304L circumvents this problem because it has a lower carbon content limit, and therefore can be subjected to welding and higher temperature applications.
- Stainless Steel Tubing for General Corrosion-Resistance: It is appropriate for applications that require corrosion resistance above other traits. Ferritic or martensitic types of steel (those made with the most chromium) are manufactured to be either heat-treated or annealed. Austenitic Stainless steels (those with high chromium and nickel contents) offer even more resistance, and can be used under the same general conditions as ferritic and martensitic types.
- Stainless Steel Pressure Pipe: It is is made from either solid chromium or a chromium and nickel combination. Types of stainless steel pressure pipe include seamless and welded pipe, electric fusion welded pipe for high-pressure applications, large diameter welded pipe for corrosive or high-temperature applications, and seamless and welded ferritic and austenitic stainless steel pipe.
- Stainless Steel Sanitary Tubing: Stainless steel sanitary tubing is used in applications where stainless steel tubing or piping must come into contact with food and other sensitive products, sanitation is a high priority; because it has high corrosion-resistance, doesn’t tarnish, and is easy to keep clean. For specific applications, different tolerances can be achieved. The grade typically used for these applications is ASTMA270.
- Stainless Steel Mechanical Tubing: In applications such as cylinders, bearings, and other hollow formed parts, stainless steel mechanical tubing is typically used. Tubing can manipulated to have a variety of cross-sectional shapes, such as square and rectangular, in addition to the more traditional, round tubing cross-section. Typically, ASTMA 511 and A554 grades are employed for mechanical tubing applications.
- Stainless Steel Aircraft Tubing: In highly-specific aircraft applications, chromium and nickel type stainless steel is used because of their heat and corrosion-resistance. Found in applications that require high-strength, stainless steel aircraft tubing can be work-hardened or welded, although work-hardened pieces shouldn’t be used with some kinds of corrosive substances. Low-carbon types of stainless steel are a common choice for welded parts. For applications that require seamless and welded tubing in larger sizes (1.6 to 125 mm in outside diameter), aircraft structural tubing is used—this type of stainless steel is manufactured according to Aerospace Material Specifications (AMS) or Military Specifications (MIL Specs).
- Aircraft Hydraulic-Line Tubing: Another type of aircraft tubing, used in aerospace applications as fuel-injection lines and hydraulic systems, and tends to be small. It is often manufactured from types 304 or 304 L stainless steel because of the steel’s high-strength, corrosion-resistance, and ductility.
Applications of Stainless Steel
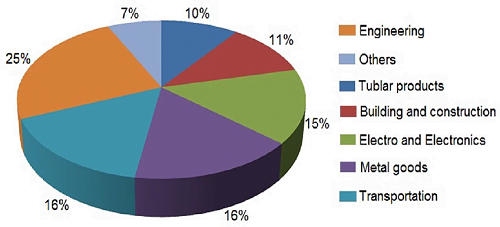
Applications of Stainless Steel
Stainless steels are used extensively in food and drink production and the chemical and energy industries; martensitics are used for cutlery and other cutting tool manufacture. Metallica is a leading stainless steel supplier in India, to various industries such as constructions, food industry, pharmaceutical industry, petrochemical industry, automotive industry, municipal and decorative purposes, etc. We produce and supply stainless steel pipe, fittings, and flanges in various grades such as:
- TP304 TP304L TP316 TP316L TP347 TP347H TP321 TP321H TP310 TP310S
- TP410 TP410S TP403
- S31803/S32205 S32750 S32760
Advantages of Stainless Steel
- Does not react or influence other materials.
- Used extensively in the food/catering divisions.
- Used widely in the medical world. E.g. Plates and screws to repair bones.
- Aesthetic Qualities: It can be polished to a satin or mirror finish.
- Dry Corrosion: Stainless steel is far more resistant to this than ordinary carbon steel.
- Grades such as 310 (25% chromium 20% nickel) were specifically developed for use at high temperatures.
- Non-contamination: Because there is no coating to break down and dissolve there is no contamination of liquids that stainless steel comes in contact with.
- Weight: As thinner sections and more innovative design structures can be used, giving cost savings on foundations and platform weights.
Difference Between Seamless and Welded Stainless Steel Pipe. How to Identify Whether a Pipe is Seamless or Welded?
Electric Resistance Welding (ERW) pipe is manufactured by rolling metal and then welding it longitudinally across its length. Seamless pipe is manufactured by extruding the metal to the desired length; therefore ERW pipe have a welded joint in its cross-section, while seamless pipe does not have any joint in its cross-section through-out its length.
In Seamless pipe, there are no welding or joints and is manufactured from solid round billets. The seamless pipe is finished to dimensional and wall thickness specifications in sizes from 1/8 inch to 26 inch OD. Applicable in for High-pressure applications such as Hydrocarbon Industries & Refineries, Oil & Gas Exploration & Drilling, Oil & Gas Transportation and Air and Hydraulic cylinders, Bearings, Boilers, Automobiles, etc.
ERW (Electric Resistance Welded) pipes are welded longitudinally, manufactured from Strip / Coil and can be manufactured upto 24” OD. ERW pipe cold formed from a ribbon of steel pulled through a series of rollers and formed into a tube which is fused through a electric charge. It is mainly used for low/ medium pressure applications such as transportation of water / oil. Common sizes for ERW Steel Pipe range from 2 3/8 inch OD to 24 inch OD in a variety of lengths to over 100 feet. Surface finishes are available in bare and coated formats and processing can be handled on site to customer specifications.
How to identify whether the pipe is seamless or welded?
If it is ASTM A53,
Type S means seamless.
Type F is furnace but welded,
Type E is Electrical resist welded.
That is how. It is the easiest way to identify whether pipe is Seamless or ERW.
Manufacturing Process of Seamless and Welded Stainless Steel Pipe
Seamless Pipes Manufacturing Process:
- Mandrel Mill Process
- Mannesmann Plug Mill Pipe Manufacturing Process
- Forged Seamless Pipe Manufacturing Process
- Extrusion Processes
They are explained below:-
- Mandrel Mill Process: – In the Mandrel Mill Process, a solid round (billet) is used. It is heated in a rotary hearth heating furnace and then pierced by a piercer. The pierced billet or hollow shell is rolled by a mandrel mill to reduce the outside diameter and wall thickness which forms a multiple length mother tube. The mother tube is reheated and further reduced to specified dimensions by the stretch reducer. The tube is then cooled, cut, straightened and subjected to finishing and inspection processes before shipment.
- Mannesmann Plug Mill Process: – In the Plug Mill Process, a solid round (billet) is used. It is uniformly heated in the rotary hearth heating furnace and then pierced by a Mannesmann piercer. The pierced billet or hollow shell is roll reduced in outside diameter and wall thickness. The rolled tube simultaneously burnished inside and outside by a reeling machine. The reeled tube is then sized by a sizing mill to the specified dimensions. From this step the tube goes through the straightener. This process completes the hot working of the tube. The tube (referred to as a mother tube) after finishing and inspection, becomes a finished product.
- Forged Seamless Pipe Manufacturing Process: – Steel Products may be manufactured either by casting or forging steel. Forged Seamless Pipe Manufacturing Process implies the application of mechanical forces to heated solid blocks of steel (such as ingots and/or billets) that are shaped into desired products permanently. They require the application of high temperatures to steel raw materials (to liquefy or make it malleable).Once this forging is done, pipe is machined to achieve final dimension. Forged pipes are generally used for the steam header. This process is used to manufacture large diameter seamless pipe that cannot be manufactured using traditional methods.
- Extrusion Processes: – Metal extrusion is a metal forming process in which a work piece, of a certain length and cross section, is forced to flow through a die of a smaller cross sectional area, thus forming the work to the new cross section. The length of the extruded part will vary, dependent upon the amount of material in the work piece and the profile extruded. Numerous cross sections are manufactured by this method. The cross section produced will be uniform over the entire length of the metal extrusion. Starting work is usually a round billet, which may be formed into a round part of smaller diameter, a hollow tube, or some other profile. Metal extrusion is a forming process, like other metal forming processes; it can be performed either hot or cold.
Welded Pipes Manufacturing Process:
Welded pipes are manufactured from plate or from continues coil or strips. To manufactured welded pipe, first, plate or coil is rolled in the circular section with the help of plate bending machine or by a roller in the case of continuous process. At the start of the welded pipe manufacturing process so called slabs or billets are cast in a steel mill. Dependent on the external dimensions and wall thickness there are different methods of producing welded pipes and tubes. Metallica’s manufacturing facilities perform three types of welding processes:
Electric Resistance Welding (ERW), Fusion Welding (EFW) and Double Submerged Arc Welding (DSAW). In the ERW and EFW manufacturing process welded pipes are formed by hot or cold rolling plate and welding the seam. In order to keep the outside (O.D.) surface of a welded pipe smooth and uniform a cutting tool called scarfing blade is used to remove the weld flash. Scarfing from the inside (I.D.) welded flash is also possible. With a heat treating at the end of the manufacturing process the weld zone of the steel pipe can be made less visible. Due to the weld seam lower operating pressures are stated in accordance with ASME compared to seamless pipes. In general welded tubes possess tighter dimensional tolerances than seamless pipes and are less costly if produced in same quantities.
- ERW or HFI / HFW pipe manufacturing: – Less thickness pipe, mainly ERW / EFW or HFW welded pipe are formed by continues rolling method. In this method, a flat metal strip from the strip coil is feed into the series of roller assembled in line. These rollers gradually form the strip in the circular section. At the end of rolling assembly, this pipe is continuously welded by welding machine. ERW/EFW and HFW are welding methods in which pipe is welded without adding filler material. However, EFW welding method can be used with filler material also. A process for producing welded tubes is Electric Resistance Welding (ERW) also known as Contact Welding. The manufacturing starts by cold-forming a coiled plate of steel with eligible thickness and certain width into a cylindrical shape. As the cylindrical plates come together, an electric current using heat merges the abutting edges together to create the final product. In HFW/HFI welding, a high-frequency current is used to create weld joints. Whereas, in EFW welding process; the external high energy electric arc is used to create a weld joint. Once the welding is done, the excess weld material from outside and inside of the pipe is removed with the help of trimmer tools. However, the product is still often referred to as ERW pipe, even though the weld may have been produced by the HFI / HFW (High Frequency Welded Pipe) process.
- EFW pipe manufacturing: – Processing of Electric Fusion Welding, also called Continuous Welding begins as coiled steel with appropriate thickness, width and weight is made. To form a continuous ribbon of steel several coils are welded together. Then the steel ribbon is heated to the necessary temperature and formed into an oval. In the next step the edges of the tube strip are permanently pressed together by rolls in order to receive a forged weld. In the last stage sizing rolls convert the welded tube into specific dimensions.
- DSAW pipe manufacturing : – In Single Seam SAW pipe, wedding is done with the help of submerged arc welding process. In this method, a welding arc is submerged in welding flux. A Continues solid filler wire is fed from the outside. The pipe is welded first inside and then from the outside. The process of producing Double Submerged Arc Welded Pipes first contains forming steel plates into cylindrical shapes. Later on the edges of the rolled plate are forged so that v-shaped notches are on the exterior and interior area of the seam. Then the pipe seam is being welded by an arc welder submerged under flux. In the case of high thickness pipe, multiple pass welding is done.
In a Spiral SAW pipe, steel plate from the de-coiler is formed in a spiral loop. This spiral loop is then welded from inside and outside of the pipe. Because of the method of manufacture, a wide variety of diameters can be produced. Spiral saw pipes are used for low-pressure services.
Whereas Straight SAW pipes are used for medium to high-pressure services. Spiral saw pipes are less costly compared to straight saw pipe.
Once the welding is completed, Weld seams are subjected to various non-destructive testing such as RT & UT to ensure the soundness of the weld material; pipes are hydro tested to ensure strength and ability to remain leak proof under pressure. In the last stage of inspection, the pipe is checked visually and dimensionally by competent inspection engineer. He will ensure that pipe is meeting the code, standard, and specification requirements. Once the Inspection engineer cleared the pipe, it will mark as per the standard requirements & send for the packaging. Once the Inspection engineer cleared the pipe; visually and dimensionally, it will mark as per the standard requirements & send for the packaging.
Various Grades of Stainless Steel, Metallica Deals in
As one of the biggest stainless steel suppliers in India, we stock and supply all major grades of stainless steel.
| Austenitic Stainless Steels | |
| 301 | High strength for roll formed structural components |
| 304, 304L, 304H | Standard 18/8 grades |
| 310, 310S, 310H | High temperature resistant grades |
| 316, 316L, 316H | Improved resistance to pitting corrosion in chloride environments |
| 321, 321H, 347 | Stabilized grades for heavy section welding and high temperature applications |
| 904L | High resistance to general corrosion, pitting and stress corrosion cracking |
| Ferritic Stainless Steels | |
| 409 | Automotive exhaust grade – weld stabilized |
| 430, 430F | Resistant to mildly corrosive environments |
| 439 | Resistant to mildly corrosive environments – weld stabilized |
| 444 | A ferritic alternative to grade 316 / 316L – weld stabilized |
| Duplex Stainless Steels | |
| 2101 | Lean duplex – economical alternative to 304 and 316 |
| 2304 | Duplex alternative to grade 316 |
| 2205 | Standard duplex stainless steel – high resistance to pitting and stress corrosion |
| 2507 | Super duplex with very high resistance to pitting and stress corrosion |
| Martensitic Stainless Steels | |
| 410 | Standard martensitic grade for low-duty hardened applications |
| 416 | Free-machining bar grade |
| 420 | Higher hardness martensitic grade for cutlery, cutting tools and dies |
| 431 | High hardness and toughness grade, primarily for shafting |
| 440A, 440B, 440C | Very high hardness grades used in cutting tools |
| Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel | |
| 630 | (17-4PH) High strength shafting grade |
Maximum Operating Temperatures of Stainless Steel Grades
Stainless steels have good strength and good resistance to corrosion and oxidation at elevated temperatures. Stainless steels are used at temperatures up to 1700° F for 304 and 316 and up to 2000 F for the high temperature stainless grade 309(S) and up to 2100° F for 310(S).
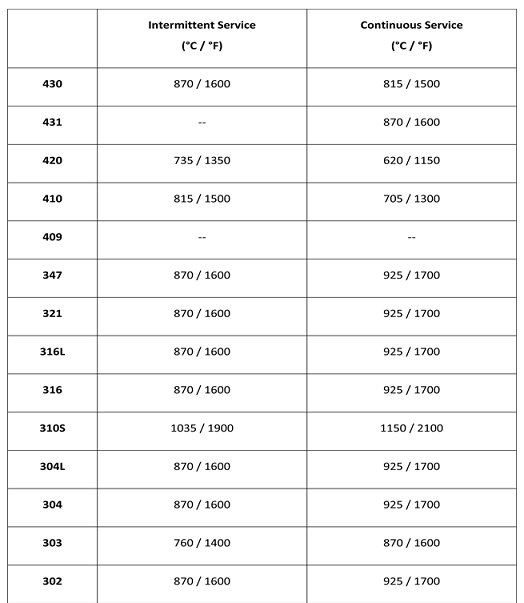
[Image Source: From Web]
Heat Process for Stainless Steel
Anneal – provides a soft low strength structure with maximum ductility
Normalize – provides a medium strength and hardness with improved ductility
Quench and Temper – Provides the maximum strength levels with good ductility and wear resistance.
Steel Pipe Sizes
Pipe size is quoted as a “Nominal Pipe Size” or NPS. The origin of the NPS numbers for smaller pipes (< NPS 12) is different to the origin for larger diameter pipes. However, all pipes of a specific NPS number have the same external or outer diameter (OD). The internal diameter will vary depending on the wall thickness of the metal. The reason for this is so that the same structural supports can be used for all piping of a specific NPS number regardless of the wall thickness.
Schedules
Steel pipe schedules are a way to describe the wall thickness of the pipe. This is a critical parameter as it is directly related to the strength of the pipe and the suitability for specific applications. A pipe schedule is a dimensionless number and is calculated based on the design formula for wall thickness, given the design pressure and allowable stress.
Examples of schedule numbers are as follows: 5, 5S, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80, 100, 120, 140, 160, STD, XS, and XXS—with the most common being schedules 40 and 80. As the schedule number increases, the wall thickness of the pipe increases. The schedule number of a pipe therefore defines the internal diameter, as the OD is fixed by the NPS number.
Testing & Inspection of Stainless Steel Pipes
Testing (Destructive, Non Destructive)
| Positive Material Identification – PMI Testing | Hydrostatic Test |
| Chemical Analysis – Spectro Analysis | Hydrogen-Induced Cracking (HIC) Test |
| Mechanical Testing Such as Tensile, Elongation, Reduction of Area | Sulfide Stress Corrosion Cracking (SSC), NACE TM 0177 |
| Micro Test | Radiography Test |
| Macro Test | Dye Penetrant Test (DP Test) |
| Hardness Test | Ultra Sonic Test (UT) |
| Pitting Resistance Test | Eddy Current Testing |
| Intergranular Corrosion (IGC) Test | Impact Test |
| Flaring Test | Bend Test |
| Flattening Test |
Inspection
- Our internal inspection reports would be provided for all the goods before shipment.
- Buyers or their associates are most welcome to visit us for personal inspect
- We regularly have inspections ongoing at our premises from internationally acclaimed Inspection Agencies such as TUV, BVIS, SGS, Llyods, DNV etc.
Prices for Stainless Steel Pipes
Prices for stainless steel pipes are directly co related to prices of the raw materials such as iron ore, metal scrap, chromium, nickel and various other alloying elements. The production cost of heat resistant stainless steel and nickel alloy plates is high as they contain high amount of nickel and chromium. Meanwhile, mild steel material is among the lowest cost steel available, followed by carbon steel, 400 series stainless steels, aluminium, alloy steel, and 300 series stainless steel. Special alloys such as titanium, Inconel, Monel and Hastelloy cost very high as the nickel, chromium and moly content is very high.
For special and discounted prices for various types of stainless steel pipes, please feel free to contact us through email, phone or whatsapp.
We are also regularly publishing our pricelist for various steel products on our blog.
Documents Provided at the time of Domestic Sales or Export of Stainless Steel Pipes
| Certificate of Origin | Raw Material Test Reports |
| Commercial Invoice | Heat Treatment Charts |
| Packing List | Quality Assurance Plan (QAP) |
| Fumigation Certificates | NABL approved Laboratory Test Reports |
| Letter of Guarantee | Material Test Certificates |
| ROHS Certificate | Certificate of Compliance/Conformity |
Price Basis for Stainless Steel Pipes
We can offer any of the following price basis depending on your requirement:
- Ex-works
- FOR Site in India
- FOB Nhava Sheva
- CFR, CIF, CPT your destination port
- Door to Door Delivery Duty Paid as well as Duty Unpaid
Delivery Time of Stainless Steel Pipes
- If the items are available in stock, we take 2 days from the date of receipt of advance payment to clear the shipment and send it to port.
- And in-case the items are not available in stock, the time taken for manufacturing depends on the size, quantity and grade.
- However we can claim the fact that we can compete with anyone in India on Delivery time and most of the time our production time is the least.
- We have tied up with strong logistic partners in India which can undertake any type of shipping activities and make sure that there is no delay in shipment.
Marking & Packing of Stainless Steel Pipes
- All our products will have complete marking details which are co-related to the test certificates we supply.
- In case of orders for cut piece of Pipes, Sheets or Round Bars, the marking is transferred from the product from which it is cut. In such cases we provide Letter confirming the marking transfer and picture of the product from which it is cut.
- All goods are packed in wooden cases or pallets.
Suppliers of Stainless Steel Pipes in India
Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, Chennai, Kolkata, Surat, Pune, Jaipur, Visakhapatnam, Kanpur, Nagpur, Lucknow, Thane, Bhopal, Indore, Pimpri Chinchwad, Patna, Vadodara, Ghaziabad, Ludhiana, Agra, Nashik, Faridabad, Meerut, Rajkot, Kalyan-Dombivli, Vasai-Virar, Varanasi, Srinagar, Aurangabad, Dhanbad, Amritsar, Navi Mumbai, Allahabad, Howrah, Ranchi, Gwalior, Jabalpur, Coimbatore, Vijayawada, Jodhpur, Madurai, Raipur, Chandigarh, Guntur, Guwahati, Solapur, Hubli–Dharwad, Mysore, Tiruchirappalli, Bareilly, Moradabad, Tiruppur, Gurgaon, Aligarh, Jalandhar, Bhubaneswar, Salem, Mira-Bhayandar, Warangal, Jalgaon, Kota, Bhiwandi, Saharanpur, Gorakhpur, Bikaner, Amravati, Noida, Jamshedpur, Bhilai, Cuttack, Firozabad, Kochi, Nellore, Bhavnagar, Dehradun, Durgapur, Asansol, Rourkela, Nanded, Kolhapur, Ajmer, Akola, Gulbarga, Jamnagar, Ujjain, Loni, Siliguri, Jhansi, Ulhasnagar, Jammu, Sangli-Miraj & Kupwad, Mangalore, Erode, Belgaum, Ambattur, Tirunelveli, Malegaon, Gaya, Thiruvananthapuram, Udaipur, Kakinada, Davanagere, Kozhikode, Maheshtala, Rajpur, Sonarpur, Rajahmundry, Bokaro, South Dumdum, Bellary, Patiala, Gopalpur, Agartala, Bhagalpur, Muzaffarnagar, Bhatpara, Panihati, Latur, Dhule, Tirupati, Rohtak, Sagar, Korba, Bhilwara, Berhampur, Muzaffarpur, Ahmednagar, Mathura, Kollam, Avadi, Kadapa, Kamarhati, Sambalpur, Bilaspur, Shahjahanpur, Satara, Bijapur, Kurnool, Rampur, Shimoga, Chandrapur, Junagadh, Thrissur, Alwar, Bardhaman, Kulti, Nizamabad, Parbhani, Tumkur, Khammam, Ozhukarai, Bihar Sharif, Panipat, Darbhanga, Bally, Aizawl, Dewas, Ichalkaranji, Karnal, Bathinda, Jalna, Eluru, Barasat, Kirari Suleman Nagar, Purnia, Satna, Mau, Sonipat, Farrukhabad, Durg, Imphal, Ratlam, Hapur, Arrah, Anantapur, Karimnagar, Etawah, Ambarnath, North Dumdum, Bharatpur, Begusarai, New Delhi, Gandhidham, Baranagar, Tiruvottiyur, Pondicherry, Sikar, Thoothukudi, Rewa, Mirzapur, Raichur, Pali, Ramagundam, Haridwar, Vijayanagaram, Tenali, Nagercoil, Sri Ganganagar, Karawal Nagar, Mango, Thanjavur, Bulandshahr, Uluberia, Katni, Sambhal, Singrauli, Nadiad, Secunderabad, Naihati, Yamunanagar, Bidhannagar, Pallavaram, Bidar, Munger, Panchkula, Burhanpur, Raurkela Industrial Township, Kharagpur, Dindigul, Gandhinagar, Hospet, Nangloi Jat, Malda, Ongole, Deoghar, Chapra, Haldia, Khandwa, Nandyal, Morena, Amroha, Anand, Bhind, Bhalswa Jahangir Pur, Madhyamgram, Bhiwani, Berhampore, Ambala, Morbi, Fatehpur, Raebareli, Mahaboobnagar, Chittoor, Bhusawal, Orai, Bahraich, Vellore, Mehsana, Raiganj, Sirsa, Danapur, Serampore, Sultan Pur Majra, Guna, Jaunpur, Panvel, Shivpuri, Surendranagar Dudhrej, Unnao, Chinsurah, Alappuzha, Kottayam, Machilipatnam, Shimla. Adoni, Udupi, Katihar, Proddatur, Saharsa, Hindupur, Sasaram, Hajipur, Bhimavaram, Kumbakonam, Dehri, Madanapalle, Siwan, Bettiah, Guntakal, Srikakulam, Motihari, Dharmavaram, Gudivada, Phagwara, Narasaraopet, Suryapet, Miryalaguda, Tadipatri, Karaikudi, Kishanganj, Jamalpur, Ballia, Kavali, Tadepalligudem, Amaravati, Buxar, Jehanabad, Aurangabad, Gangtok
Export Sales of Stainless Steel Pipes
- America: Antigua and Barbuda, Argentina, Aruba, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Cayman Islands, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Grenada, Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Puerto Rico, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, United States, Uruguay, Venezuela
- Europe – Albania, Andorra, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Euro area, Faroe Islands, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Isle of Man, Italy, Kosovo, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Malta, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine, United Kingdom
- Africa – Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea Bissau, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mauritius, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Swaziland, Tanzania, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe
- Asia – Afghanistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Brunei, Cambodia, China, East Timor, Georgia, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Lebanon, Macao, Malaysia, Maldives, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Palestine, Philippines, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Korea, Sri Lanka, Syria, Taiwan, Tajikistan, Thailand, Turkmenistan, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, Yemen
- Australia – Australia, Fiji, Kiribati, New Caledonia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Vanuatu
Over 1000 Tons in Stock for Stainless Steel Pipes!
Steel Pipes Dealers, Original MTR’s Provided with All Materials
As one of the biggest stainless steel pipe stockholder and supplier in India, Metallica carries inventory of over 1000 tons in its warehouses in Mumbai, Maharashtra India. We sell our stainless steel pipe products throughout India, and to international clients. We can supply our stainless steel tube products not only in industry-standard lengths and diameters, but also in custom length and diameters.
Certification of Stainless Steel Pipes
Manufacturers issue a Material Test Report or Mill Test Report to validate that the product meets the chemical analysis and mechanical properties specification. The MTR will contain all relevant data to the product and will accompany the product through its lifecycle.
The following are typical parameters that may be recorded on an MTR:
- Chemical composition including carbon content, alloys, and sulfur
- Material size, weight, identification, and grade
- Material heat number, which ties back to the processing batch
- Mechanical properties like tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation
